Are you curious about the secret to unlocking the fountain of youth? The search for effective anti-aging solutions is never-ending.
Among the intriguing options available, rapamycin has captured the attention of scientists and enthusiasts alike. But how does it work, and more importantly, what is the right rapamycin dosage for anti-aging? If you’re eager to uncover how this groundbreaking compound could potentially turn back the clock on your biological age, you’re in the right place.
We’ll explore the science behind rapamycin, its potential benefits, and how you can consider incorporating it into your anti-aging regimen. Get ready to discover if rapamycin is the key to a younger, more vibrant you.
Rapamycin Basics
Understanding the basics of rapamycin is essential before considering its use for anti-aging. This drug has gained attention for its potential to extend lifespan and improve healthspan. Let’s break down what rapamycin is, how it influences aging, and the science behind its longevity effects.
What Is Rapamycin?
Rapamycin is a drug originally used to prevent organ transplant rejection. It’s also known as sirolimus and works by suppressing the immune system. Beyond this, researchers found it has remarkable effects on cellular processes linked to aging.
You might wonder why a drug meant for transplant patients is connected to living longer. The answer lies in its ability to target specific pathways that control cell growth and metabolism.
How Rapamycin Affects Aging
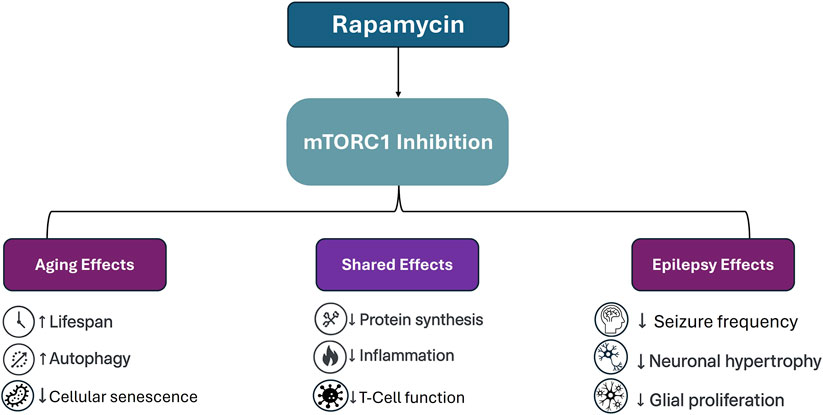
Rapamycin slows down the aging process by influencing a key protein complex called mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin). This protein acts like a switch that controls cell growth and repair.
By inhibiting mTOR, rapamycin encourages the body to focus on maintenance and repair instead of rapid growth. This shift can reduce age-related diseases and improve overall health.
Think about it this way: rapamycin helps your cells “take a break” from overworking and spend more time fixing damage. Could this be the reason why users report increased vitality?
Mechanism Behind Longevity Benefits
The main mechanism behind rapamycin’s anti-aging effects is mTOR inhibition. When mTOR is less active, cells improve their ability to clean up damaged components through a process called autophagy.
Autophagy acts like a cellular recycling system, removing waste that accumulates over time. This cleanup helps maintain healthier cells and tissues.
Additionally, rapamycin influences metabolism and reduces inflammation, both crucial factors in aging. Understanding these mechanisms helps you see why rapamycin dosage and timing matter for maximizing benefits.

Credit: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Dosage Principles
Understanding the dosage principles of rapamycin is crucial for anyone considering it for anti-aging purposes. The right amount can maximize benefits while minimizing risks. Let’s break down how dosage works and what you should consider before starting.
Common Dosage Ranges
Typical rapamycin doses for anti-aging are much lower than those used in transplant medicine. Most users take between 1 mg to 5 mg per week. This low dosing helps reduce side effects but still activates pathways linked to longevity.
Some people report benefits with as little as 1 mg every two weeks, while others find 5 mg once a week effective. Are you someone who responds better to smaller, more frequent doses or larger, less frequent ones? Finding your sweet spot is key.
Frequency And Timing
Rapamycin is often taken weekly or biweekly rather than daily. This intermittent dosing helps avoid immune suppression and other unwanted effects. Many find taking it in the evening aligns better with the body’s natural rhythms.
Timing can also depend on your lifestyle. For example, if you work night shifts, you might adjust the timing to fit your sleep schedule. How you space doses can impact how your body reacts over time.
Factors Influencing Dosage
Your age, weight, and health status affect how much rapamycin you should take. Older adults may need lower doses due to slower metabolism. If you have existing health conditions or take other medications, dosage adjustments may be necessary.
Genetics also play a role in how your body processes rapamycin. Some people metabolize the drug faster and may require higher doses to see effects. Have you considered getting blood tests to monitor your response? This can guide safer, more personalized dosing.
Safety And Side Effects
Rapamycin shows promise in anti-aging, but safety is vital. Understanding side effects helps users make informed decisions. Careful dosage and monitoring reduce risks. Awareness of who should avoid rapamycin protects health.
Potential Risks
- Lowered immune system function
- Increased risk of infections
- Possible mouth sores or ulcers
- Changes in blood sugar levels
- Raised cholesterol or triglycerides
- Delayed wound healing
These effects depend on dose and individual response. Close medical supervision is important.
Managing Side Effects
- Start with low doses and increase slowly
- Report any infections or unusual symptoms immediately
- Maintain a healthy diet to support immune health
- Regular blood tests to check sugar and lipid levels
- Keep good oral hygiene to prevent mouth sores
- Discuss all medications with your doctor
Who Should Avoid Rapamycin?
- People with active infections
- Those with weak immune systems
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- Individuals with liver or kidney problems
- Anyone allergic to rapamycin or similar drugs
Consult a healthcare professional before starting rapamycin therapy.

Credit: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Personalizing Dosage
Personalizing your rapamycin dosage is crucial for maximizing its anti-aging benefits while minimizing risks. Everyone’s body reacts differently, so a one-size-fits-all approach won’t work. Understanding how factors like age, health, and other supplements influence your dose can help you tailor a plan that fits your unique needs.
Age And Health Considerations
Your age plays a big role in how rapamycin affects you. Younger individuals might need lower doses since their bodies are more resilient, while older adults may require adjusted doses to avoid side effects.
Health conditions also matter. If you have immune system issues or chronic illnesses, you should be extra cautious with rapamycin. Talking to your doctor about your specific health profile can guide safer dosing decisions.
Monitoring And Adjustments
Starting with a low dose and carefully monitoring your response is a smart strategy. Keep an eye on side effects like fatigue or mouth sores, which can signal the need for dose tweaks.
Regular blood tests can track your body’s reaction over time. Adjust your dose based on these results and how you feel to find the sweet spot between effectiveness and safety.
Combining With Other Supplements
Rapamycin doesn’t work in isolation. Some supplements might boost its benefits, while others could interfere or increase side effects.
- Adding antioxidants like vitamin C might support overall health but check for interactions.
- Supplements that suppress the immune system can increase risks when combined with rapamycin.
- Always research or consult a healthcare professional before mixing supplements.
Have you noticed how your body reacts when combining supplements with rapamycin? Tracking these changes can help you personalize your anti-aging strategy more effectively.
Current Research Insights
Research on rapamycin’s role in anti-aging is growing rapidly. Scientists study how it affects lifespan and health. These studies help understand safe and effective dosages. They also explore potential benefits and risks. Ongoing research aims to unlock clearer guidelines for use.
Studies On Rapamycin And Longevity
Animal studies show rapamycin can extend lifespan. Mice treated with rapamycin lived longer and stayed healthier. The drug slows aging in many body systems. It reduces inflammation and improves cell repair. These effects support the idea of rapamycin as an anti-aging agent.
Human Trials And Results
Human research is in early stages but promising. Some trials focus on immune health and age-related diseases. Rapamycin has improved vaccine responses in older adults. Dosages in trials are carefully controlled to avoid side effects. More data is needed to confirm long-term safety and benefits.
Future Directions
Future studies will refine optimal dosage and timing. Researchers plan larger and longer human trials. They aim to understand how rapamycin works with other treatments. Personalized approaches may tailor dosage to individual needs. These efforts will improve safe use of rapamycin for aging.

Credit: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Practical Tips For Use
Using rapamycin for anti-aging requires more than just picking up a bottle and starting. You need a clear plan to make the most of its potential benefits while minimizing risks. Practical tips can help you use rapamycin safely and effectively, keeping your health and progress in focus.
Starting Rapamycin Safely
Begin with the lowest dose possible to see how your body reacts. Many users start with a small dose, such as 1 mg once a week, to minimize side effects. Pay attention to how you feel and avoid increasing your dosage too quickly.
Consider spacing out doses to reduce the chance of immune suppression. Some people take rapamycin every two weeks instead of weekly. This approach can help your body adjust and maintain balance.
Have you thought about how your current medications or supplements might interact with rapamycin? It’s important to check this before starting to avoid unexpected reactions.
Tracking Progress
Keep a journal to record your dosage, any side effects, and changes in energy or wellbeing. This simple habit can reveal patterns and help you and your doctor make informed decisions.
Use objective measures like blood tests to monitor immune function and other markers related to aging. Regular testing can catch issues early and confirm whether rapamycin is working for you.
Apps or spreadsheets can help you maintain consistency and remind you when to take your dose. Staying organized reduces the risk of missed doses or accidental overdosing.
Consulting Healthcare Providers
Talk openly with your doctor before starting rapamycin, especially if you have underlying health conditions. Their expertise can guide you toward a safe dosage tailored to your needs.
Bring your tracking journal to appointments to provide clear data on how rapamycin affects you. This information makes your consultations more productive and personalized.
Ask questions about long-term use and potential risks. Understanding what to expect helps you stay in control of your anti-aging journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Recommended Rapamycin Dosage For Anti-aging?
The typical anti-aging rapamycin dose ranges from 1 to 5 mg weekly. Dosage depends on individual health, age, and goals. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting.
How Often Should Rapamycin Be Taken For Anti-aging?
Rapamycin is usually taken once weekly for anti-aging benefits. This schedule balances effectiveness and minimizes side effects. Follow medical advice for personalized frequency.
Are There Risks With Rapamycin Anti-aging Dosage?
Yes, improper rapamycin dosing can cause immune suppression and side effects. Monitoring by a healthcare provider ensures safe use. Always adhere to prescribed doses.
Can Rapamycin Dosage Vary By Age Or Health Status?
Yes, dosage varies based on age, weight, and health conditions. Older adults or those with health issues may require adjusted doses. Professional guidance is essential.
Conclusion
Rapamycin shows promise for slowing aging effects in the body. Finding the right dosage is key to staying safe and effective. Start low and adjust carefully with medical advice. Keep track of how your body responds over time. Balance benefits with possible risks for the best results.
Always talk to a healthcare provider before starting rapamycin. Taking small steps helps protect your health. Aging well takes patience and smart choices.